Pic Structure Of Human With All Muscles And Bones Name : DK Find Out! | Fun Facts for Kids on Animals, Earth ... : Here we explain the major skeletal muscles, muscle structure, fibre types, contractions and sliding filament theory.
Pic Structure Of Human With All Muscles And Bones Name : DK Find Out! | Fun Facts for Kids on Animals, Earth ... : Here we explain the major skeletal muscles, muscle structure, fibre types, contractions and sliding filament theory.. The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system1) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move the bones provide stability to the body. The human body contains 206 bones, which provide structure, allow movement and protect vital organs. All the bones, when they are joined together, make the skeletal system of a body. The human body is made up of many cells, so it is an example of a multicellular organism. Striated / skeletal muscle (causing the movement of bones/limbs).
They are the mandible, vomer, two maxillae every human skull has fractals or sutures of the skull. A regional atlas of the human body is sobotta, j. Skeletal muscle is a voluntary muscle, which means that we can actively control its function. The bone that doesn't move and the muscle is anchored to. The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system1) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move the bones provide stability to the body.

Created and produced by qa international.
A skeleton is the hard structure that protects the internal organs of a living thing. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Osteoclasts help remodel injured bones and create pathways for nerves and blood vessels to travel through. Hand, bone, finger, vein, wrist, dorsal, human bones, metacarpal, human hands, prehensile this week was about the study of the human bone structure. Humans have three different kinds of muscle: The integrated action of joints, bones, and skeletal muscles produces obvious movements such as walking and running. Shoulder girdle consists of the clavicle (collar bone) and the scapula (shoulder blade) which generally move together. The human skeleton is composed of the total set of bones that provide the human body a multifunctional structure. Although skeletal muscle cells come in different shapes and sizes, the main structure of a skeletal muscle cell remains the same. Lies in a small pocket of bone at the skull base called the sella turcica. The structure of the human brain as compared to other mammals is bigger and more advanced. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement. Many prenatal bones fuse postnatal developing neonate and child (about 275).
The structure of human muscles and bones. Bones and muscles under the skin. Our bones, muscles, and joints form our musculoskeletal system and enable us to do everyday physical activities. Hand, bone, finger, vein, wrist, dorsal, human bones, metacarpal, human hands, prehensile this week was about the study of the human bone structure. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
Muscles act by contraction which results in their shortening and pulls on tendons.
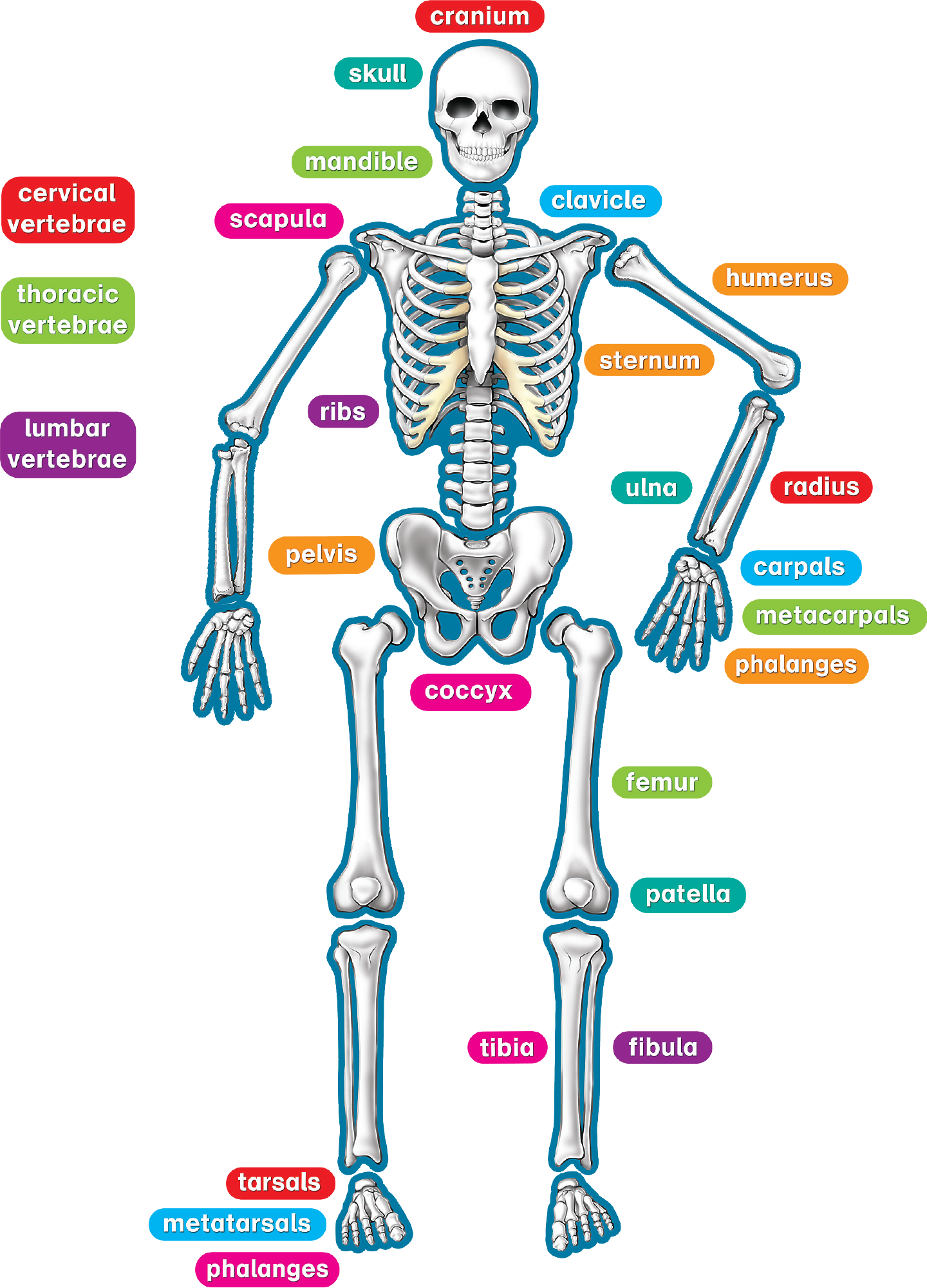
Human muscles enable movement it is important to understand what they do in order to diagnose sports injuries and prescribe rehabilitation exercises. Many prenatal bones fuse postnatal developing neonate and child (about 275). Although skeletal muscle cells come in different shapes and sizes, the main structure of a skeletal muscle cell remains the same. Humans have three different kinds of muscle: Skeletons can be inside the body or outside the body. They are the mandible, vomer, two maxillae every human skull has fractals or sutures of the skull. Human anatomy bones and structures. The bone that doesn't move and the muscle is anchored to. A skeleton is the hard structure that protects the internal organs of a living thing. The skull is formed from 8 bones that fuse together. A human skeleton with the names of the bones labelled. Field guide to the human body™. The human body contains 206 bones, which provide structure, allow movement and protect vital organs.
Download unlimited stock videos at $99/month. It is made of involuntary cardiac muscles, and this is why the heart continues beating. The two main forms of ossification occur in different bones, intramembranous (eg skull) and endochondral. The muscle system is responsible for movement of the human body, posture, movement of substances inside the body andfor the generation of body heat. Translating skeletal structure names can help you find & remember them.

It supports the body and allows movement.
I have also worked from my own drawings anatomy, and physicians. Field guide to the human body™. The structure of striated, or skeletal, muscle. Muscles act by contraction which results in their shortening and pulls on tendons. Bones and muscles under the skin. Muscle is so named because, it resembles a mouse, with their tendons representing the tail. Action of muscles muscles do not suddenly snap from a state of relaxation to one of contraction. This 6th edition of anatomy: Muscles keep bones in place and also play a role in the movement of bones. The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system1) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move the bones provide stability to the body. Here we explain the major skeletal muscles, muscle structure, fibre types, contractions and sliding filament theory. The structure of human muscles and bones. The structure of the human brain as compared to other mammals is bigger and more advanced.

Komentar
Posting Komentar